Radioactive Decay Radioactive substances such as Uranium and Radium spontaneously disintegrate while emitting radiation in the form of α or ß particles and γ rays. The loss of an alpha particle result in the formation of a new element, that occupy a position on the Periodic Table, two places to the…
Showing posts with label gcse maths. Show all posts
Showing posts with label gcse maths. Show all posts
Wednesday, 14 May 2025
Monday, 31 March 2025
Iteration for A Level Maths: staircase method & cobweb method
E.g. f(x) = x² - x - 4 When the above is rearranged in the form of x = g(x), it is said to be in iterative form.
x² - x - 4 = 0 x = 1 + x/4
x n+1 = 1 + x n / 4
If x n is known, x n+1 can be calculated. The initial value to trigger off the iterative process is found by looking for change in sign of…
Sunday, 15 December 2024
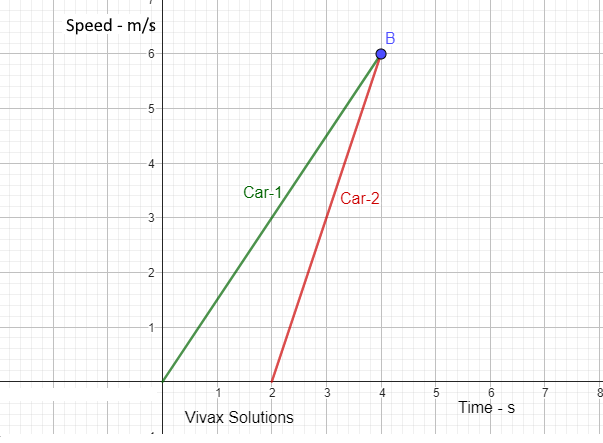
Practise straight line graphs for GCSE, IGCSE and GCE - OL: fully interactive
This applet generates a straight line at the click of a button. From the line on a grid, you can calculate both the gradient and intercept, if the latter is visible. Otherwise, you need to find the gradient of the line and the coordinates of any point through which the line passes. E.g. If the gradie…
Basic Integration: finding the area under a curve by a GeoGebra applet - fully interactive
With the following GeoGebra applet, you can find out the area under a curve by integration - interactively. All you need to do is to move the two sliders to points of your choice and tick the checkbox for answer to appear. The function used in this case is a quadratic function. Enjoy, learn and pro…
Saturday, 19 October 2024
Linear and Geometric Sequences for GCSE, IGCSE & A Level
E.g.1 : Find the nth term of the sequence: 3, 7, 11, 15, ... The common difference is 4. Let N = an + b, where N is the nth term and a an b are constants to be found. 3 = a(1) + b = a + b 7 = a(2) + b = 2a + b Solving the two equations simultaneously, we get a = 4 and b = -1 So, the nth term, N = 4n - 1 …
Saturday, 7 September 2024
Conquer GCSE Maths Challenges: Practise Tough Questions for Free
Are you ready to test your GCSE/IGCSE maths skills to the limit?
Saturday, 13 April 2024
The exponential graph
The exponential function is a special exponential function; the gradient of any point on the curve is the same as the value of the function at that point.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Popular Posts
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics and Mechanics - Time: 40 minutes Created and Programmed by Vivax Solutions St...
-
In the above animation, five points on the wave are considered for the explanation. The fully interactive applet is given below for you ...
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics - electricity - Time: 40 minutes Created and Programmed by Vivax Solutions Star...
-
Denary to Binary Conversion Denary to binary conversion is a fundamental concept in computer science and digital electronics. It involves t...
-
Multiple Choice Questions - A Level Physics - Capacitors - Master capacitor concepts with this interactive A Level Physics quiz! Whether...
TOP CATEGORIES
- a level computer science (11)
- a level physics (42)
- gcse maths (29)
- gcse physics (14)
- general physics (11)
Featured Post
Labels
a level computer science
(11)
A Level Maths
(27)
a level physics
(42)
featured
(4)
GCSE Computer Science
(9)
gcse maths
(29)
gcse physics
(14)
general physics
(11)
math
(1)
physics
(1)